7.1 ARRAY LIST METHODS
- ArrayList is a resizeable array
- ArrayLists are dynamic meaning that its size can be altered as necessary
- Instead of creating a new array of a different size and copying the data from the initial array to the new one, we can use ArrayLists
- To use an arrayList it is necessary to be imported from the java util package
VOCABULARY
Static: Once initialized, size cannot be changed (arrays)
Dynamic: Size of list can be changed at any time (arrayLists)

import java.util.ArrayList; // Import the ArrayList class
// Declare and initialize an ArrayList of integers
ArrayList<Integer> numbersList = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(numbersList);
[]
- ArrayLists are created in a similar manner as other object classes
- in the <> when declaring an arrayList is the data type it will contain. (integer, string, etc…)
- Can also make an arraylist without declaring the data type but it can prevent error detection
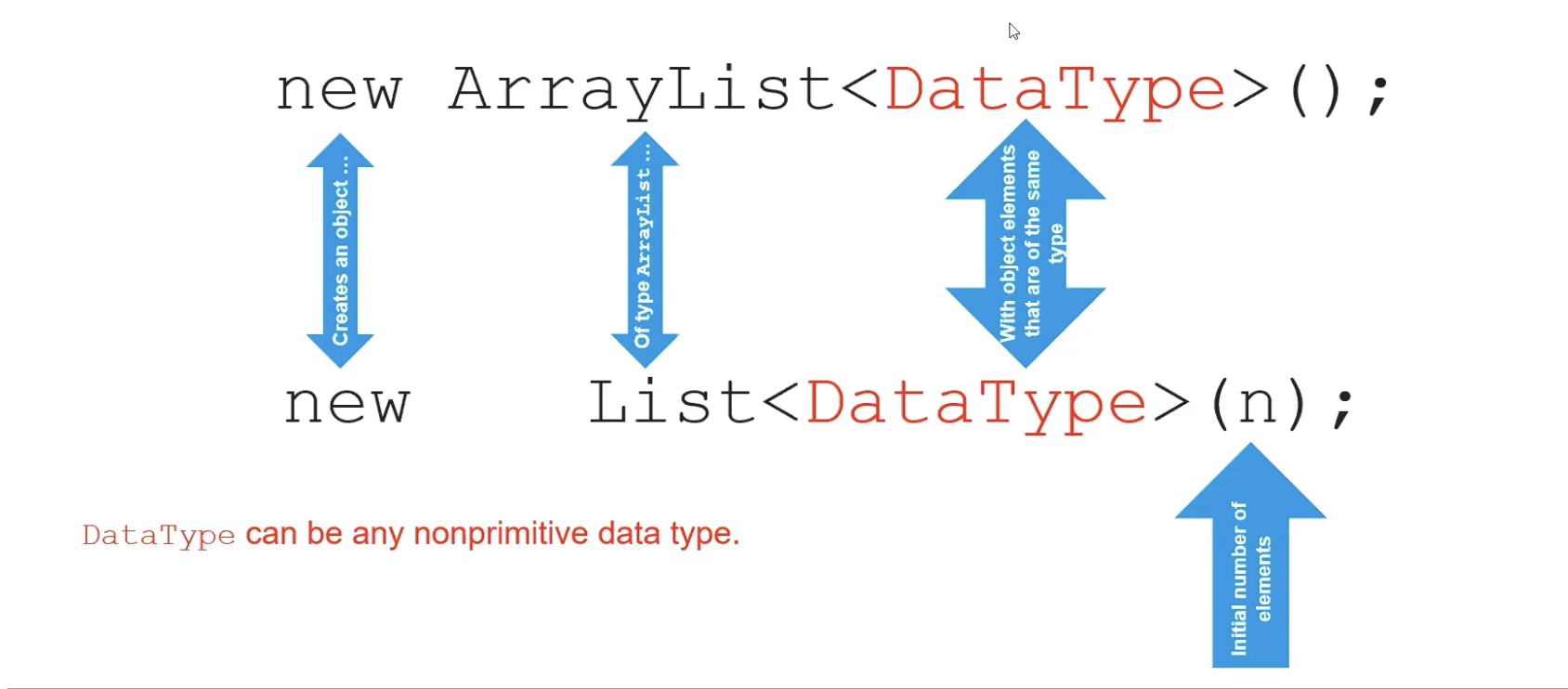
ArrayList<String> wordList = new ArrayList<String>(); // with data type
ArrayList blankList = new ArrayList(); // without data type
System.out.println(wordList);
[]
7.2 ARRAY LIST METHODS
- You can get the number of items in an ArrayList using the .size() method
- All arrayLists start with 0
ArrayList<String> sizeList = new ArrayList<String>();
System.out.println(sizeList.size());
0
-
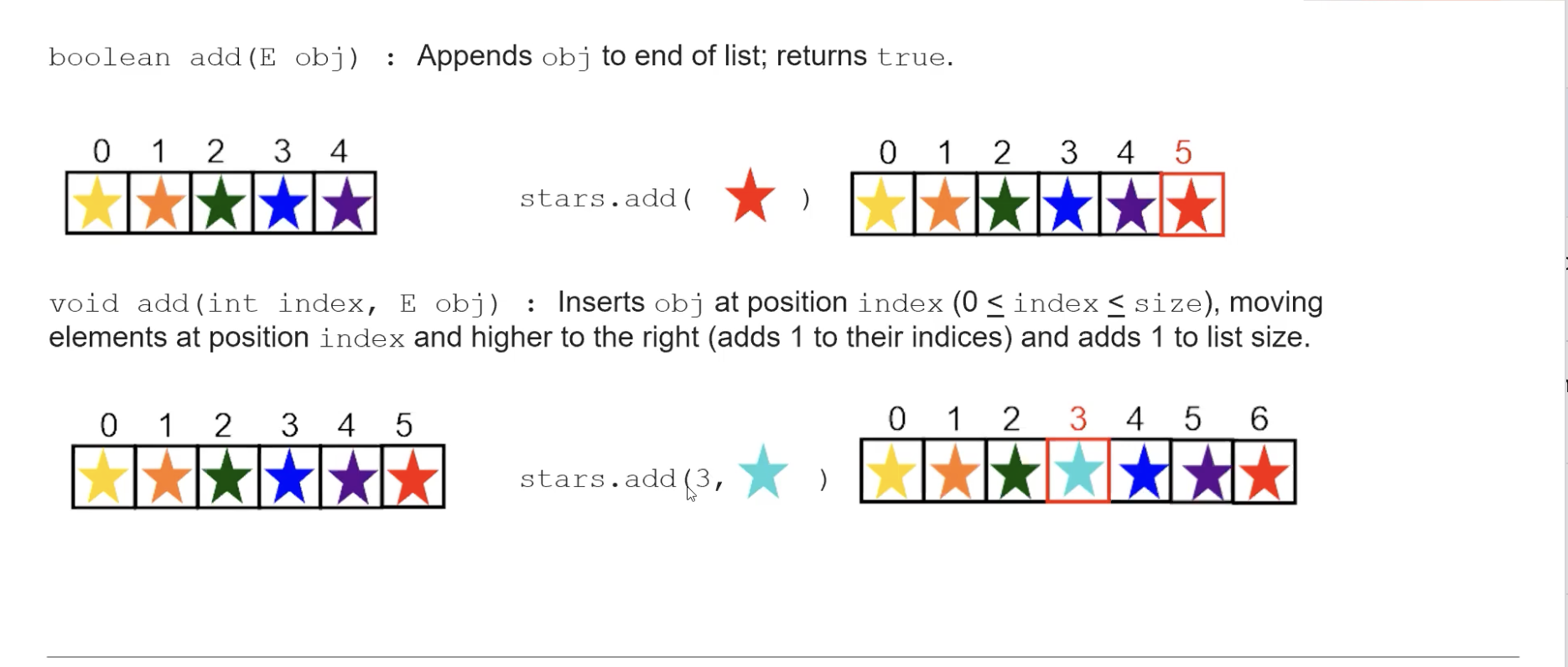
You can add values to an array list by using add method. syntax: list.add(obj)
-
How you would join the end of a line to buy a ticket (similar concept)
ArrayList<String> addList = new ArrayList<String>();
addList.add("CSA");
System.out.println(addList.size());
System.out.println(addList);
1
[CSA]
-
int size() - Returns the count of elements within the list.
-
boolean add(E obj) - Appends the object obj to the end of the list and returns true.
-
void add(int index, E obj) - Inserts obj at the specified index, shifting elements at and above that position to the right (incrementing their indices by 1) and increasing the list’s size by 1.
-
E get(int index) - Retrieves the element at the given index in the list.
-
E set(int index, E obj) - Replaces the element at the specified index with obj and returns the previous element at that index.
-
E remove(int index) - Deletes the element at the specified index, shifting all subsequent elements one index to the left, reducing the list’s size by one, and returning the removed element.
-
Java allows the generic ArrayList
, where the generic type E specifies the type of element. -
When ArrayList
is specified, the types of the reference parameters and return type when using the methods are type E. -
ArrayList
is preferred over ArrayList because it allows the compiler to find errors that would otherwise be found at runtime.
ArrayList<Integer> a1 = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(a1.size());
ArrayList<Double> a2 = new ArrayList<>();
a2.add(1.0);
a2.add(2.0);
a2.add(3.0);
System.out.println(a2);
a2.remove(2.0);
System.out.println(a2);
0
[1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
[1.0, 3.0]
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Create ArrayList of Integers
ArrayList<Integer> a1 = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("Initial size of a1: " + a1.size());
// Create ArrayList of Doubles and add elements
ArrayList<Double> a2 = new ArrayList<>();
a2.add(1.0);
a2.add(2.0);
a2.add(3.0);
System.out.println("Initial a2: " + a2);
// Remove element at index 2
a2.remove(2); // Use index for removal, not value
System.out.println("After removing element at index 2: " + a2);
// Insert element at index 1
a2.add(1, 1.5);
System.out.println("After inserting 1.5 at index 1: " + a2);
// Retrieve element at index 2
Double elementAtIndex2 = a2.get(2);
System.out.println("Element at index 2: " + elementAtIndex2);
// Replace element at index 1
Double previousElement = a2.set(1, 1.75);
System.out.println("After replacing element at index 1: " + a2);
System.out.println("Previous element at index 1: " + previousElement);
// Get the size of a2
int sizeOfA2 = a2.size();
System.out.println("Size of a2: " + sizeOfA2);
Initial size of a1: 0
Initial a2: [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
After removing element at index 2: [1.0, 2.0]
After inserting 1.5 at index 1: [1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
Element at index 2: 2.0
After replacing element at index 1: [1.0, 1.75, 2.0]
Previous element at index 1: 1.5
Size of a2: 3
POPCORN HACKS 7.1 & 7.2 Create an ArrayList of Strings with the following elements: “Apple”, “Banana”, “Cherry”, “Date”, “Elderberry”. Complete the following tasks using the ArrayList methods you’ve learned:
- Task 1: Print the size of the ArrayList.
- Task 2: Add a new element “Fig” to the end of the list.
- Task 3: Insert “Grape” at index 2.
- Task 4: Replace the element at index 4 with “Guava”.
- Task 5: Remove the element at index 1.
- Task 6: Retrieve and print the element at index 3.
At the end of each task, print the current state of the ArrayList to verify the result.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an ArrayList of Strings
ArrayList<String> fruits = new ArrayList<>();
fruits.add("Apple");
fruits.add("Banana");
fruits.add("Cherry");
fruits.add("Date");
fruits.add("Elderberry");
// Task 1: Print the size of the ArrayList
System.out.println("Task 1: Size of the ArrayList: " + fruits.size());
System.out.println("Current ArrayList: " + fruits);
// Task 2: Add a new element "Fig" to the end of the list
fruits.add("Fig");
System.out.println("Task 2: Added 'Fig'");
System.out.println("Current ArrayList: " + fruits);
// Task 3: Insert "Grape" at index 2
fruits.add(2, "Grape");
System.out.println("Task 3: Inserted 'Grape' at index 2");
System.out.println("Current ArrayList: " + fruits);
// Task 4: Replace the element at index 4 with "Guava"
fruits.set(4, "Guava");
System.out.println("Task 4: Replaced element at index 4 with 'Guava'");
System.out.println("Current ArrayList: " + fruits);
// Task 5: Remove the element at index 1
fruits.remove(1);
System.out.println("Task 5: Removed element at index 1");
System.out.println("Current ArrayList: " + fruits);
// Task 6: Retrieve and print the element at index 3
String elementAtIndex3 = fruits.get(3);
System.out.println("Task 6: Element at index 3: " + elementAtIndex3);
}
}
ArrayListExample.main(null);
Task 1: Size of the ArrayList: 5
Current ArrayList: [Apple, Banana, Cherry, Date, Elderberry]
Task 2: Added 'Fig'
Current ArrayList: [Apple, Banana, Cherry, Date, Elderberry, Fig]
Task 3: Inserted 'Grape' at index 2
Current ArrayList: [Apple, Banana, Grape, Cherry, Date, Elderberry, Fig]
Task 4: Replaced element at index 4 with 'Guava'
Current ArrayList: [Apple, Banana, Grape, Cherry, Guava, Elderberry, Fig]
Task 5: Removed element at index 1
Current ArrayList: [Apple, Grape, Cherry, Guava, Elderberry, Fig]
Task 6: Element at index 3: Guava